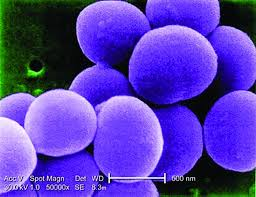
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that commonly colonises human skin and mucosa.
Normally the bacteria cause no harm and those colonised with S. aureus remain asymptomatic. S. aureus can however lead to serious infections when bacteria spread to the bloodstream, this may occur when then skin is broken, for example following surgery or a medical procedure. S. aureus may cause a range of illness including skin and wound infections, infected eczema, abscesses or joint infections, endocarditis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis, urinary tract infections and bacteraemia.
Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) is a cytotoxin produced by some strains of Staphylococcus aureus that causes leukocyte destruction and tissue necrosis.